Spatially Balanced Sample Designs in R with `spsurvey::grts()`
We've been using spatially balanced stratified study designs more frequently at work these days. They are a good way to make probabilistic inference over large areas. A popular method of creating these designs is using the R function spsurvey::grts(). The following is a basic (very basic) explainer of how to get up and running with grts() function and what it is. But a bit about GRTS and spatially balanced study design before we get coding.
What is GRTS (Generalized Random Tessellation Stratified sampling)?
Generalized Random Tessellation Stratified sampling is a method to draw points randomly across a stratified polygon or line (doesn't necessarily need to be stratified). If you want to get into the weeds you can read the original paper for the design here. For me, it's only important that I understand that spatially balanced survey designs are probability-based survey designs that specify where to sample so that inferences from the sample apply to the entire population. In other words, its a method to randomly draw points so that they cover an entire population or area. Non-spatially balanced random samples, another popular method, have a tendency to cluster points and have no method to make sure the entire population is covered.
How to implement spsurvey::grts()
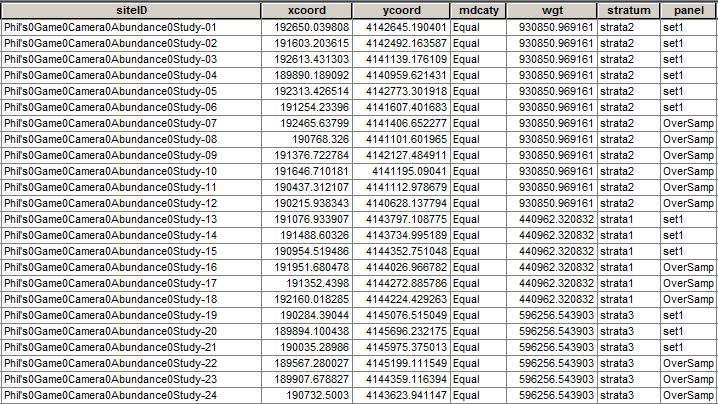
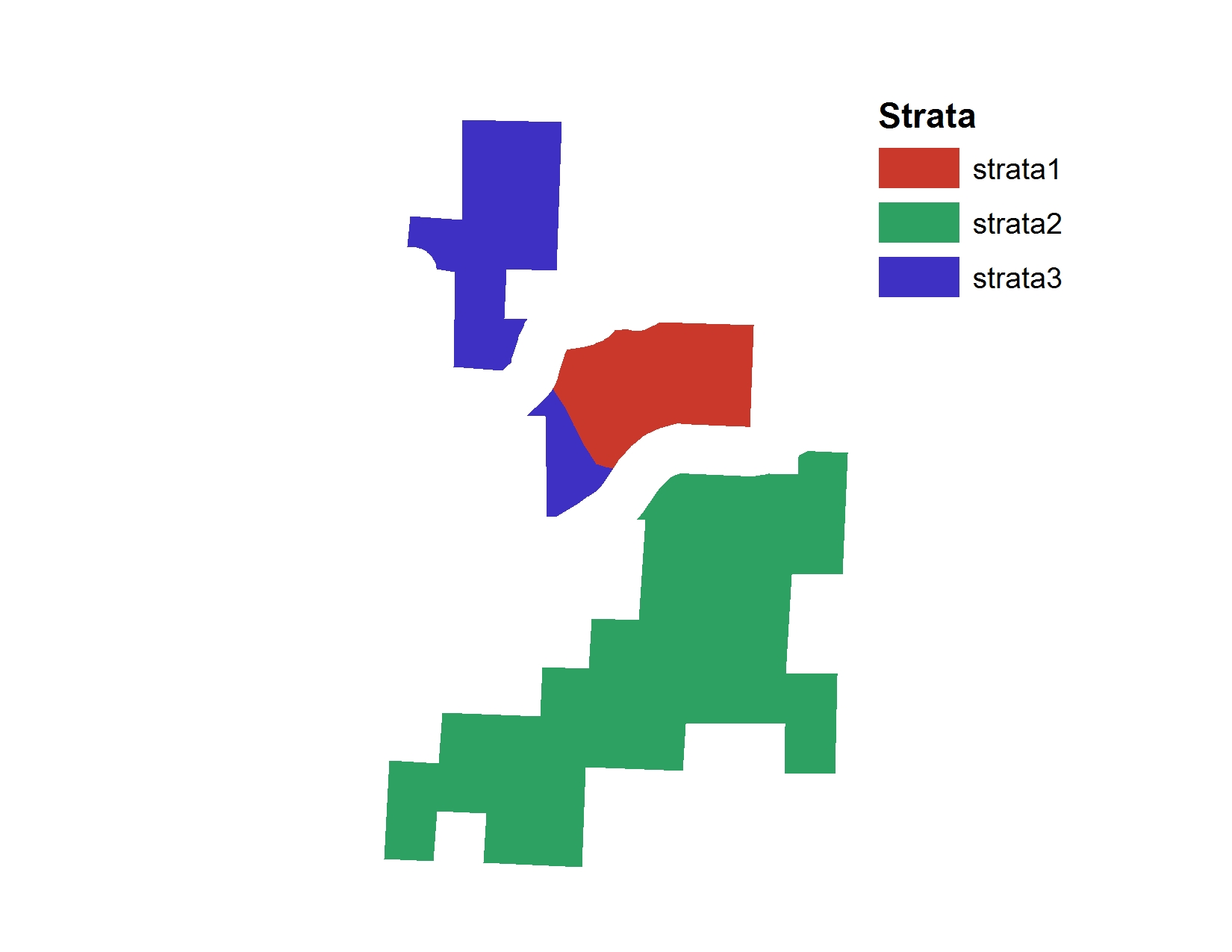
Step 1 - Make a Shapefile in ArcGIS with a field that represents your strata Make a shapefile with your desired strata. We want to monitor wildlife in a recreation area across three strata. Strata 1 has no recreation trails, strata 2 has newly constructed recreation trails and strata 3 has historic recreation trails going back 20 plus years. All are in important habitats for big game.
You need to provide grts() a shapefile with a strata variable. I used ArcMap to do this but you can also use QGIS or other free GIS software. The result of our strata looks like this:
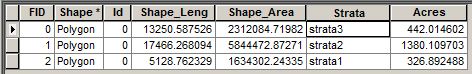
Again: it's really important that the polygons are in a single shapefile and there is a field that represents what strata you want. The shapefile tabular data should look something like this:
Step 2 - R Code: Create a GRTS sample design
One of the trickiest parts for me was understanding the first function parameter of grts(), design. The documentation for design reads:
Named list of stratum design specifications which are also lists. Stratum names must be subset of values in stratum argument. Each stratum list has four components:
And then lists the details for panel, seltype, caty.n and over. Take a peak at the documentation for more details here.
design<-list(
strata2 = list(panel=c(set1=6), seltype="Equal", over=6),
strata1 = list(panel=c(set1=3), seltype="Equal", over=3),
strata3 = list(panel=c(set1=3), seltype="Equal", over=3)
)In my case I only needed panel, and over parameters. Let's break this down. You need to store your list() of design features in a variable that you will later call in the grts() function. In this case we've named it design. Next, within the list, you need a list element that has a name that is the same as your shapefile strata. In my case the strata are called strata1, strata2, and strata3, so I have three list elements with those names. Next each element needs a panel, seltype, and over value. seltype can be left on the default "Equal".
- panel represents the number of points that you want in the strata. You can have multiple panels per strata. For example if you have a multiple year study, you might want to have panels that represent each year. That would look like:
list(panel = c(2019 = 6, 2020 = 6, 2021 = 6)). This would draw 6 spatially balanced points throughout the year. In the above example though we will only have one panel because we will put out points over one year. - over is if you can't get to one of the points in the panel, over will provide you with an oversample of points. In our case we used the same amount of points for over as we drew in our panel.
Step 3 - Drawing the sample
The code first then we can break it down:
## From the last step
design<-list(
strata2 = list(panel=c(set1=6), seltype="Equal", over=6),
strata1 = list(panel=c(set1=3), seltype="Equal", over=3),
strata3 = list(panel=c(set1=3), seltype="Equal", over=3)
)
## GRTS code
test.sample <- grts(design=design,
DesignID="Phil's Game Camera Abundance Study",
type.frame="area",
src.frame="shapefile",
in.shape="strata/final_strata_acres.shp",
stratum="Strata",
shapefile=TRUE,
out.shape="points/for_blog.shp")And the resulting points draw:
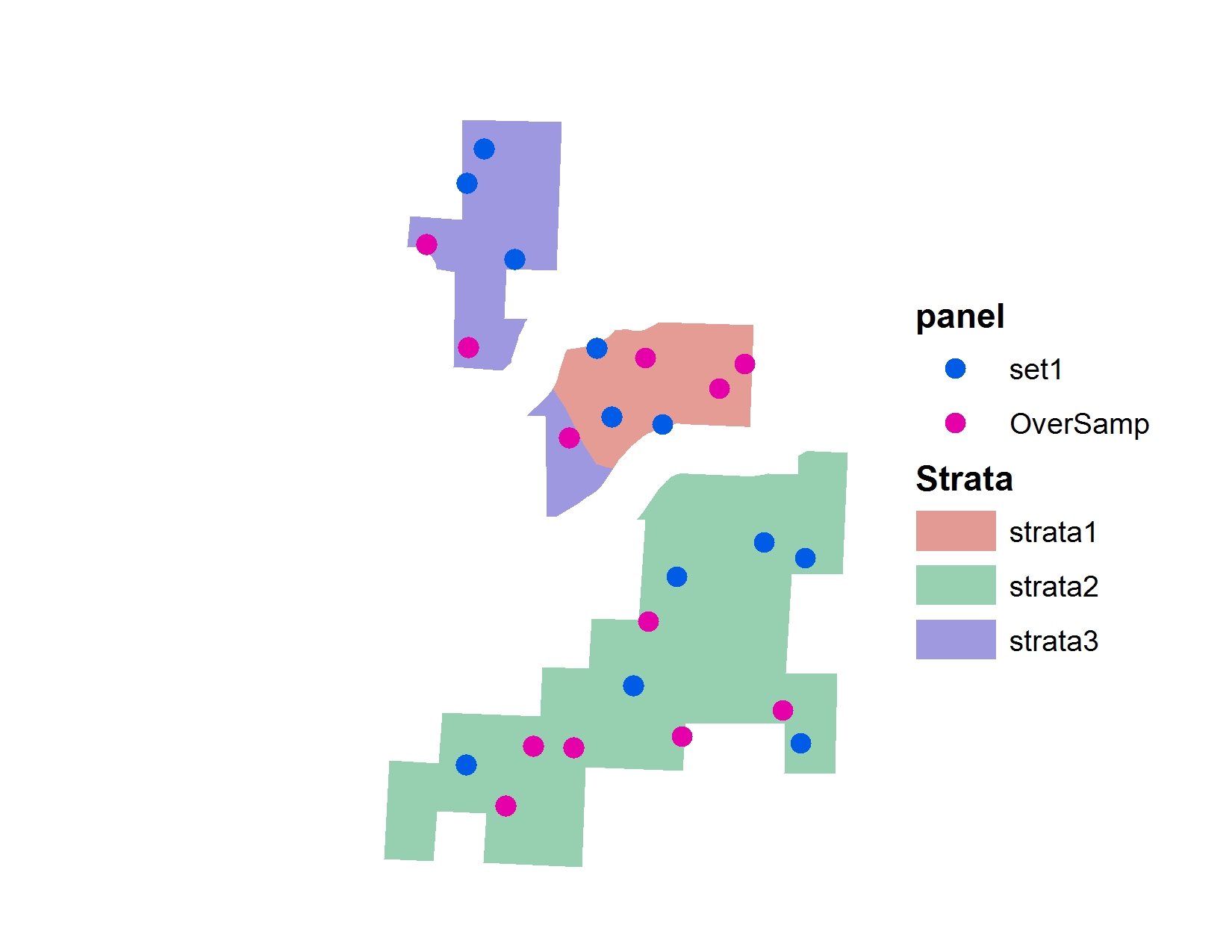
And table:
Let's break this down:
- design is the design that we made in step 2.
- DesignID is whatever you want the name of the study to be.
- type.frame should be area if you are inputting polygons. Can also be linear if you are inputting lines.
- src.frame in most cases this should be shapefile.
- in.shape the location of the shapefile with strata in it.
- stratum the field that includes your stratum information.
- shapefile TRUE/FALSE. TRUE means create output shapefile.
- out.shape Destination and name of output.